HSE Scientists Explain How to Identify Brain Areas Critical for Language Function During Surgery
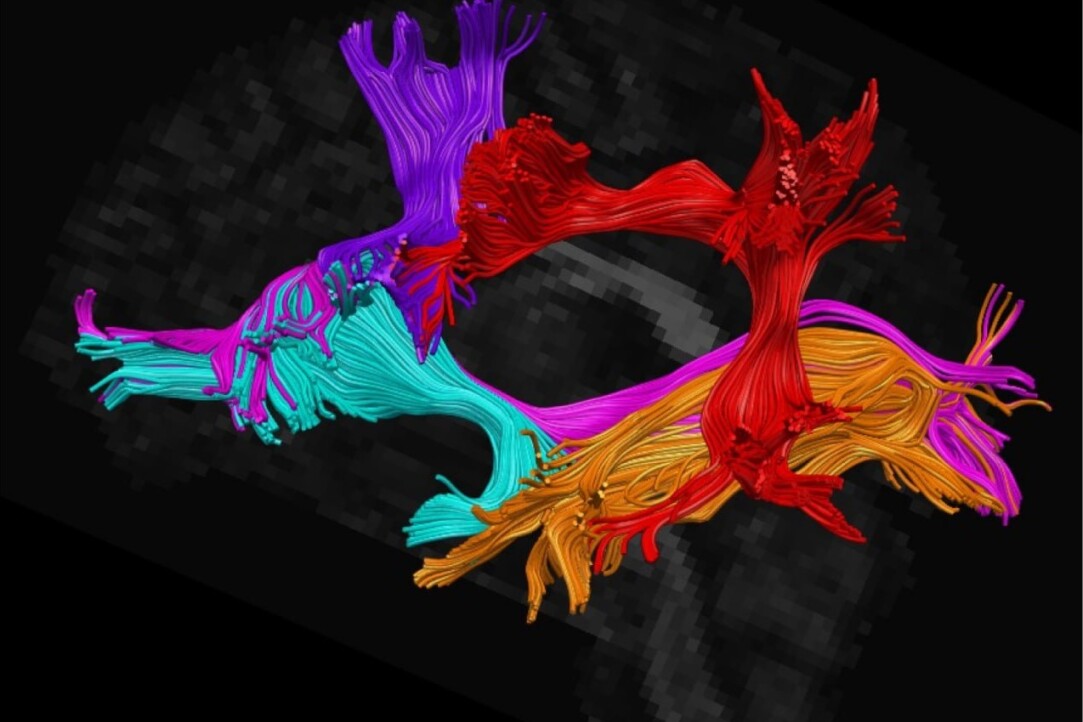
The HSE Centre for Language and Brain conducted a course on tractography, a method that enables visualisation of key brain connections and helps surgeons avoid damaging language-critical areas during surgery. The course was attended by neurosurgeons and radiologists from Moscow and other Russian regions who are interested in methods of preoperative language mapping.
Tractography is a technique for constructing 3D models of the brain’s pathways using diffusion-weighted MRI data. In the brain’s white matter, water primarily diffuses along nerve fibres, and this directionality can be reconstructed using specialised algorithms. One such method is diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), which allows researchers to assess the degree of water molecule diffusion alignment and to map the brain’s white matter tracts.
During the training course, participants not only discussed various theoretical issues related to preoperative and intraoperative mapping of language function and tracts but also gained hands-on experience in manually reconstructing models using the TrackVis software tool, based on pre-processed structural MRI images.
A dedicated lecture focused on linguistic tests for intraoperative mapping, a technique used by clinicians to identify language areas during surgery.
'Localising language function is a critical step in planning surgical interventions for patients with lesions in the language-dominant hemisphere. Experts at the Centre for Language and Brain have accumulated significant experience in preoperative language mapping, which minimises the risk of complications and improves the effectiveness of surgical interventions. We are pleased to share our knowledge and practical recommendations with our surgical colleagues to advance modern neurosurgery and improve the quality of patient care,' said Anna Komissarenko, Junior Research Fellow at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
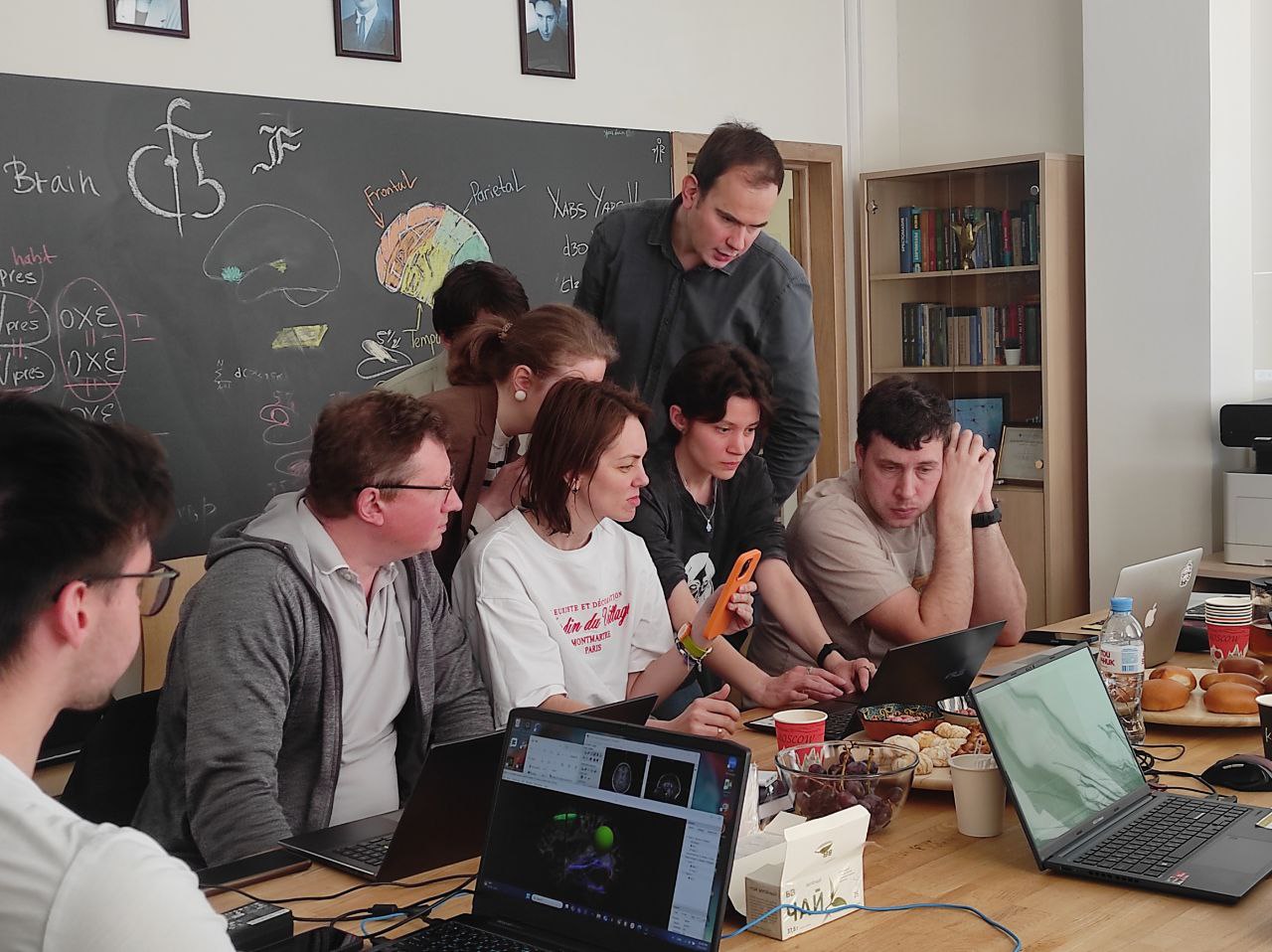

The HSE Centre for Language and Brain has extensive expertise in providing linguistic support for neurosurgical patients. An important focus of the centre’s work is the development of specialised linguistic tests to identify functionally significant language areas during the planning and performance of neurosurgical operations. The centre’s specialists are investigating how the brain’s language function reorganises in cases of tumours and epilepsy, with special emphasis on the role of white matter pathways in supporting language function. The findings are used in both research and clinical practice—during preoperative mapping and intraoperative language monitoring. The practical course generated great interest among participants and served as a platform for interdisciplinary dialogue between neurolinguists and clinicians.
Anastasia Parshunina, neurosurgeon
'During surgery, it is essential to balance the radicality of the operation with the patient’s functional status. When removing a tumour near the language area in a patient with intact language function, it is crucial that the patient retains the ability to speak and understand speech after treatment. Therefore, the ability to reconstruct tracts is essential for preoperative treatment planning and for understanding the relationship between the tumour and functionally significant structures. The course deepened our understanding of anatomical principles and demonstrated the potential of 3D modelling for preoperative planning. We are thankful to the course organisers. During the two-day course, we gained valuable theoretical knowledge and practical skills in reconstructing pathways using the TrackVis software.
The Centre for Language and Brain thanks all course participants and invites everyone to stay updated on upcoming courses and educational programmes.
See also:
HSE Researchers Offer Guidance to Prevent Undergraduate Burnout
Researchers at the HSE Institute of Education have identified how much time students should ideally devote to their studies, extracurricular activities, and personal life to maintain strong academic performance without compromising their mental health. An analysis of responses from 2,753 students, combined with their actual academic results, revealed several risk factors—such as excessive homework—as well as positive factors, including sufficient sleep, regular exercise, and moderate participation in projects. Based on these findings, the researchers developed practical recommendations for both students and universities. The paper has been published in the European Journal of Education.
When a Virus Steps on a Mine: Ancient Mechanism of Infected Cell Self-Destruction Discovered
When a virus enters a cell, it disrupts the cell’s normal functions. It was previously believed that the cell's protective response to the virus triggered cellular self-destruction. However, a study involving bioinformatics researchers at HSE University has revealed a different mechanism: the cell does not react to the virus itself but to its own transcripts, which become abnormally long. The study has been published in Nature.
Researchers Identify Link between Bilingualism and Cognitive Efficiency
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has discovered that knowledge of a foreign language can improve memory performance and increase automaticity when solving complex tasks. The higher a person’s language proficiency, the stronger the effect. The results have been published in the journal Brain and Cognition.
Lost Signal: How Solar Activity Silenced Earth's Radiation
Researchers from HSE University and the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences analysed seven years of data from the ERG (Arase) satellite and, for the first time, provided a detailed description of a new type of radio emission from near-Earth space—the hectometric continuum, first discovered in 2017. The researchers found that this radiation appears a few hours after sunset and disappears one to three hours after sunrise. It was most frequently observed during the summer months and less often in spring and autumn. However, by mid-2022, when the Sun entered a phase of increased activity, the radiation had completely vanished—though the scientists believe the signal may reappear in the future. The study has been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics.
‘Engagement in the Scientific Process’: HSE Launches Master’s Programme in Neurobiology
The HSE University Academic Council has elected to launch a new Master's programme in Neurobiology for students majoring in Biology. Students of the programme will have access to unique equipment and research groups, providing them with the knowledge and experience to pursue careers in science, medicine and pharmacy, IT and neurotechnology, and education and HR services.
Banking Crises Drive Biodiversity Loss
Economists from HSE University, MGIMO University, and Bocconi University have found that financial crises have a significant negative impact on biodiversity and the environment. This relationship appears to be bi-directional: as global biodiversity declines, the likelihood of new crises increases. The study examines the status of populations encompassing thousands of species worldwide over the past 50 years. The article has been published in Economics Letters, an international journal.
Scientists Discover That the Brain Responds to Others’ Actions as if They Were Its Own
When we watch someone move their finger, our brain doesn’t remain passive. Research conducted by scientists from HSE University and Lausanne University Hospital shows that observing movement activates the motor cortex as if we were performing the action ourselves—while simultaneously ‘silencing’ unnecessary muscles. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
Russian Scientists Investigate Age-Related Differences in Brain Damage Volume Following Childhood Stroke
A team of Russian scientists and clinicians, including Sofya Kulikova from HSE University in Perm, compared the extent and characteristics of brain damage in children who experienced a stroke either within the first four weeks of life or before the age of two. The researchers found that the younger the child, the more extensive the brain damage—particularly in the frontal and parietal lobes, which are responsible for movement, language, and thinking. The study, published in Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, provides insights into how age can influence the nature and extent of brain lesions and lays the groundwork for developing personalised rehabilitation programmes for children who experience a stroke early in life.
Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.