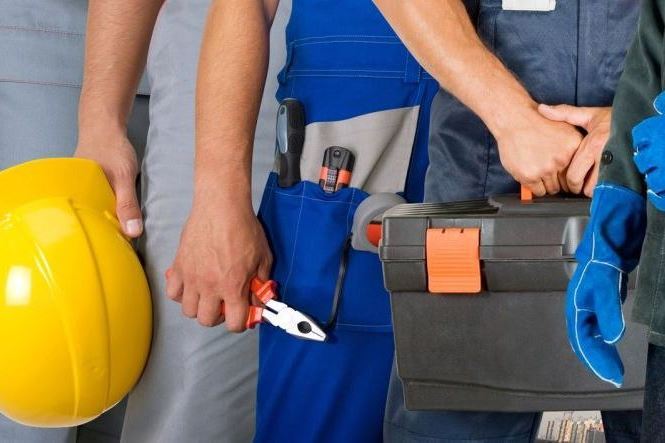
Russians with Degrees: Where Are They Employed?
Russia has a problem with the under-utilisation of education. Almost 30% of employees with university degrees report no connection whatsoever between their training and current occupation, according to Elena Varshavskaya's paper 'Where and in what jobs highly educated Russians work.'
-%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B3%20%D0%B4%D0%BE%D1%84%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%B8%D0%BD.jpg)
Alcoholism May Be Caused by Dynamical Dopamine Imbalance
Researchers from the Higher School of Economics, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, Indiana University and the Russian Academy of Sciences Nizhny Novgorod Institute of Applied Physics have identified potential alcoholism mechanisms, associated with altered dopaminergic neuron response to complex dynamics of prefrontal cortex neurones affecting dopamine release.
Sberbank and HSE Institute of Education to Cooperate on Landmark 21st Century Skills Project
Sberbank’s Charity Foundation and the HSE Institute of Education have recently agreed to cooperate on a milestone 21st century skills research and development project. With multiple representatives of the academic and business communities, among others, this collaborative endeavour aims to deliver visible improvements to Russia’s education system. In particular, the project will involve devising a clear approach to identifying, evaluating, and deploying core next-generation skills and competencies that consider national socioeconomic and educational contexts alongside global best practice.
.jpg)
Which Crimes Do Russian Police Investigate?
In deciding whether or not they will register a particular incident or offence and whether they will investigate it according to the rules or in exchange for a bribe, Russian law enforcement officers tend to act from one of four different perspectives: state, departmental, commercial or professional, according to Elena Berdysheva's study 'Varying Worth of Crimes in the Eyes of Policemen in Russia'.
.jpg)
Motor Cortex Influences Word Comprehension
Researchers from HSE, Northumbria University, and Aarhus University have experimentally confirmed the hypothesis, whereby comprehension of a word’s meaning involves not only the ‘classic’ language brain centres but also the cortical regions responsible for the control of body muscles, such as hand movements. The resulting brain representations are, therefore, distributed across a network of locations involving both areas specialised for language processing and those responsible for the control of the associated action. The results have been published in the journal Neuropsychologia.
Who Studies Russian Science and How?
On February 8, Russian Science Day, the Higher School of Economics, along with the Russian Federal State Statistics Service (Rosstat) and the Ministry of Education and Science, released its annual statistical data book on the state of science, technology, and innovation. Below, the Director of the HSE Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge and HSE First Vice Rector Leonid Gokhberg discusses how research on science in Russia is advancing.
.jpg)
HSE Experts Investigate How Order Emerges From Chaos
Igor Kolokolov and Vladimir Lebedev, scientific experts from HSE’s Faculty of Physics and the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of Russian Academy of Sciences, have developed an analytical theory, which binds the structure of coherent vortices formed due to inverse cascades in 2-D turbulence with the statistical properties of hydrodynamic fluctuations. Uncovering this link can be useful in identifying the causes of the particular characteristics of such atmospheric phenomena as cyclones and anticyclones. Their research is presented in an article published in the ‘Journal of Fluid Mechanics’.
Student Research Competition 2016 Winners Awarded at HSE
This year students from other Russian and international universities competed against HSE students. The new HSE project ‘Scientific Battles’ was also announced at the award ceremony.
-%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%D1%8B%20%D1%81%20%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%88%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BC.jpg)
Who Finances Charities
The belief that the non-profit sector is mainly supported by private donations is nothing but a myth. According to Natalia Ivanova's study Foreign Experience of Government's Impact on Philanthropy and Its Applicability in Russia, government support accounts for a substantial part of charity budgets.
.jpg)
One’s Ability to Make Money Develops Before Birth
Researchers from the Higher School of Economics have shown how the level of perinatal testosterone, the sex hormone, impacts a person’s earnings in life. Prior research confirms that many skills and successes are linked to the widely known 2D:4D ratio, also knows as the digit ratio. This is the ratio of the index and ring fingers, and it is considered a reflection of the level of perinatal testosterone, the male hormone of the mother that acts on the development of the offspring during pregnancy.