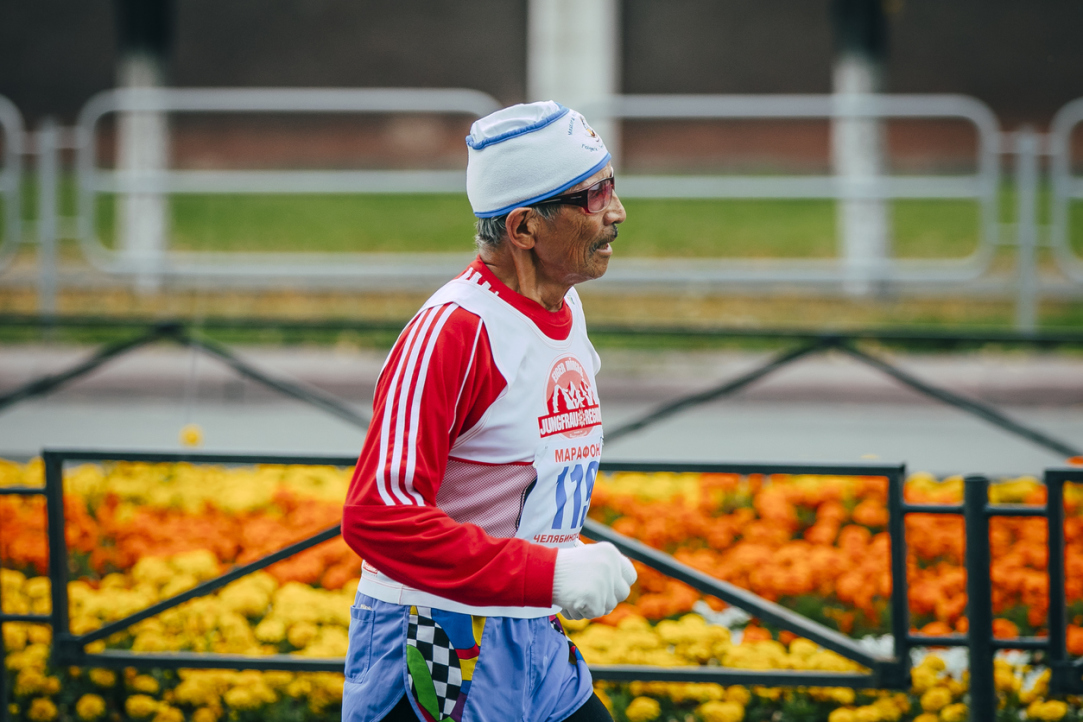

Unfit: Why Seniors Don’t Care about Their Health
Seniors in Russia are not responsive to public promotion of healthy living. Their behaviours follow eight different patterns, and a healthy lifestyle is far from being the most popular one. Only 17% of elderly people live what can be termed a 'healthy' lifestyle, Elena Selezneva discovered. The results of the study were presented at the XIX April International Academic Conference on Economic and Social Development at HSE.
Complex Issues of Identity in the Former Soviet Union Countries
The HSE Institute for Social Policy held an event entitled ‘Demographic Challenges of the 21st Century’ on 13 June 2017. At the event, Lauren Woodard, PhD candidate, Department of Anthropology, University of Massachusetts, presented her report ‘Politics of Return: Resettlement of Compatriots Programme in Primorsky Territory’. Here she talks to HSE News about the event, her research, and her interest in the complex issues of identity in Russia and the Former Soviet Union.
-%D0%BF%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B5%D1%80%D1%8B%20%D0%BD%D0%B0%20%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B5.jpg)
Five Scientific Facts about Older Russians
Older Russians are generally less healthy that their peers in Europe, the US, and other BRICS countries. Poor health is one of the barriers to remaining active and enjoying a well-deserved rest after retirement age. The second most common problem affecting elderly Russians is having to share a home with children and grandchildren, while a lack of social engagement and limited social connections come third on the list of barriers to active aging in Russia. According to researchers, the Russian elderly have social potential, but rarely use it.
.jpg)
Ageing Can Drive Progress
Twenty years from now, the number of retired persons worldwide will have grown by 600 million, almost double the current number. Life expectancy will have increased, bringing new economic challenges. Yet the growing number of seniors can also stimulate important breakthroughs in medicine, biotechnology, nanotechnology, cognitive sciences and robotics, according to the report 'Global Population Ageing and the Threat of Political Risks in the Light of Radical Technological Innovation in the Coming Decades.'
Who Feels Poor in Russia
The level of education, the size of the settlement, and the social status can all seriously affect the chance of feeling poor in Russia. These are the findings by experts of the HSE Institute for Social Policy, revealed as part of their regular Monitoring of the Social and Economic Situation and Well-being of the Population.

More Effort Needed to Integrate Migrants
At a time when industrially developed countries are facing migration pressure, Russia needs to take a fresh look at immigration to assess its geopolitical benefits and prevent inherent social risks; a smart migrant integration policy can provide a solution.
Small Towns Risk Losing Young People
Russian small towns risk being depleted of young people, as three-quarters of school leavers are planning to migrate to regional centres, Moscow or St. Petersburg in search of a better life, while just 4% are prepared to stay in their home communities.
Migrants Give More Births Than Locals
Women who have moved to another part of the country tend to have higher fertility than those who stay in the same community all their lives. Relocation often improves a woman's life circumstances and broadens her choice of marriage partner, thus supporting her reproductive intentions, according to Svetlana Biryukova, Senior Research Fellow of the HSE Center for Studies of Income and Living Standards, and Alla Tyndik, Leading Research Fellow at the RANEPA.
Drawn by Moscow’s Cultural Appeal, U.S. Student Chooses HSE to Embark on Research Career
On January 29, Thomas Espy, a student in the Population and Development Master’s programme at HSE, presented a report entitled ‘Mapping Xenophobia in Russia’. During his presentation, he highlighted his paper’s linear analysis of xenophobic attacks in the Russian Federation and a network analysis focusing on nationalist groups, as well as recommended areas of focus for Russian policymakers.
Traditional Family Is in Revival
The Russian family has been becoming more demographically heterogeneous over recent years. Some of the families follow the trend of having many children: women more often give birth to a third and fourth child, and the gap between births is decreasing, which makes the evolution of the family faster. At the same time, younger generations are inclined to postpone marriage and having their first child, which leads either to later motherhood or to childlessness. This means that two opposite trends are developing; along with the growing share of ‘Western-type’ families, with postponed parenthood and fewer children, there is a revival of the traditional family with more children, Sergey Zakharov, Deputy Director of the HSE Institute of Demography, reported.
Registration is open until April 1, 2025