Tickling the Nerves: Why Crime Content is Popular
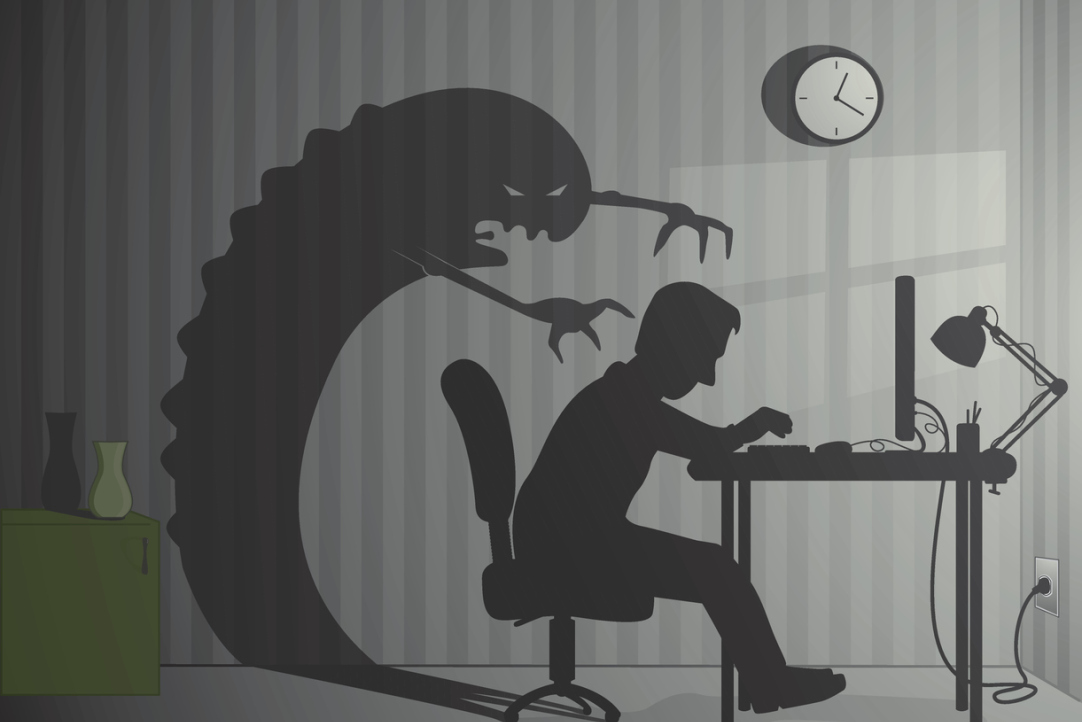

Consumers of content about serial killers watch and read it to experience intense emotions that are often lacking in everyday life and to understand the reasons that drive people to commit crimes. However, such content does not contribute to increased aggression. These conclusions were drawn by sociologists from HSE University. The results of their study have been published in Crime, Media, Culture: An International Journal.
Research on the modern media market shows that content about serial killers is popular worldwide, spanning films, true crime series, short videos, and written materials detailing crimes, investigations, and the biographies of those involved.
English sociologist Abby Bentham and Canadian sociologist Kevin Haggerty note that people perceive stories about serial killers as a form of entertainment that allows them to experience intense emotions. Canadian sociologist and philosopher Ryan Broll suggests that this is also a way for individuals to escape their own real-life problems.
However, some have expressed concerns that an obsession with stories about serial killers could lead to increased violence. To explore this question, researchers from HSE—Oksana Mikhailova, Darya Osokina, Lev Lyubich, and Ekaterina Gulina—conducted a series of in-depth interviews to study the motives driving Russian youth to consume crime content. A total of 26 young men and women aged 18 to 36 from 14 Russian cities were interviewed.
The main questions revolved around what type of media content about serial killers they liked, how they discovered it, and what they considered when choosing a film, video, or podcast. The respondents included fans of fictional TV shows, series, documentaries, true crime podcasts, books, popular science articles, videos, and social media posts.
The researchers focused specifically on the motives for consuming media content rather than its impact on the audience. The responses indicate that interest in violent content is not driven by a desire to witness violence itself and does not provoke a desire to commit violence in real life.
The study identified two types of motives driving the consumption of content about serial killers: cognitive and emotional. Cognitive motives involve a desire to understand the motives of criminals, linking their actions to childhood trauma, psychological problems, and other factors. This helps viewers better understand the causes of human behaviour. On the other hand, content about serial killers provides a way to experience intense emotions, often compensating for a lack of excitement in everyday life.

Oxana Mikhaylova
‘Interest in stories about serial killers, whether in the form of series or podcasts, is not a sublimation of cruelty. The respondents did not justify the actions of serial killers. On the contrary, they stated that such crimes should be prevented,’ notes Oxana Mikhailova, Research Fellow at the Centre for Modern Childhood Research at HSE’s Institute of Education.
The researchers emphasise that interest in such narratives is usually driven by curiosity and a search for new experiences. These findings could help psychologists develop support programmes for young people experiencing emotional hunger or stress.
See also:
Internal Clock: How Heart Rate and Emotions Shape Our Perception of Time
Our perception of time depends on heart rate—this is the conclusion reached by neuroscientists at HSE University. In their experiment, volunteers watched short videos designed to evoke specific emotions and estimated each video's duration, while researchers recorded their heart activity using ECG. The study found that the slower a participant's heart rate, the shorter they perceived the video to be—especially when watching unpleasant content. The study has been published in Frontiers in Psychology.
Scientists Identify Personality Traits That Help Schoolchildren Succeed Academically
Economists from HSE University and the Southern Federal University have found that personality traits such as conscientiousness and open-mindedness help schoolchildren improve their academic performance. The study, conducted across seven countries, was the first large-scale international analysis of the impact of character traits on the academic achievement of 10 and 15-year-olds. The findings have been published in the International Journal of Educational Research.
HSE Scientists Reveal How Disrupted Brain Connectivity Affects Cognitive and Social Behaviour in Children with Autism
An international team of scientists, including researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, has for the first time studied the connectivity between the brain's sensorimotor and cognitive control networks in children with autism. Using fMRI data, the researchers found that connections within the cognitive control network (responsible for attention and inhibitory control) are weakened, while connections between this network and the sensorimotor network (responsible for movement and sensory processing) are, by contrast, excessively strong. These features manifest as difficulties in social interaction and behavioural regulation in children. The study has been published in Brain Imaging and Behavior.
Similar Comprehension, Different Reading: How Native Language Affects Reading in English as a Second Language
Researchers from the MECO international project, including experts from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, have developed a tool for analysing data on English text reading by native speakers of more than 19 languages. In a large-scale experiment involving over 1,200 people, researchers recorded participants’ eye movements as they silently read the same English texts and then assessed their level of comprehension. The results showed that even when comprehension levels were the same, the reading process—such as gaze fixations, rereading, and word skipping—varied depending on the reader's native language and their English proficiency. The study has been published in Studies in Second Language Acquisition.
Mortgage and Demography: HSE Scientists Reveal How Mortgage Debt Shapes Family Priorities
Having a mortgage increases the likelihood that a Russian family will plan to have a child within the next three years by 39 percentage points. This is the conclusion of a study by Prof. Elena Vakulenko and doctoral student Rufina Evgrafova from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences. The authors emphasise that this effect is most pronounced among women, people under 36, and those without children. The study findings have been published in Voprosy Ekonomiki.
Scientists Discover How Correlated Disorder Boosts Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a unique state of matter in which electric current flows without any energy loss. In materials with defects, it typically emerges at very low temperatures and develops in several stages. An international team of scientists, including physicists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that when defects within a material are arranged in a specific pattern rather than randomly, superconductivity can occur at a higher temperature and extend throughout the entire material. This discovery could help develop superconductors that operate without the need for extreme cooling. The study has been published in Physical Review B.
Scientists Develop New Method to Detect Motor Disorders Using 3D Objects
Researchers at HSE University have developed a new methodological approach to studying motor planning and execution. By using 3D-printed objects and an infrared tracking system, they demonstrated that the brain initiates the planning process even before movement begins. This approach may eventually aid in the assessment and treatment of patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s. The paper has been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Civic Identity Helps Russians Maintain Mental Health During Sanctions
Researchers at HSE University have found that identifying with one’s country can support psychological coping during difficult times, particularly when individuals reframe the situation or draw on spiritual and cultural values. Reframing in particular can help alleviate symptoms of depression. The study has been published in Journal of Community Psychology.
Scientists Clarify How the Brain Memorises and Recalls Information
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has demonstrated for the first time that the anterior and posterior portions of the human hippocampus have distinct roles in associative memory. Using stereo-EEG recordings, the researchers found that the rostral (anterior) portion of the human hippocampus is activated during encoding and object recognition, while the caudal (posterior) portion is involved in associative recall, restoring connections between the object and its context. These findings contribute to our understanding of the structure of human memory and may inform clinical practice. A paper with the study findings has been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Researchers Examine Student Care Culture in Small Russian Universities
Researchers from the HSE Institute of Education conducted a sociological study at four small, non-selective universities and revealed, based on 135 interviews, the dual nature of student care at such institutions: a combination of genuine support with continuous supervision, reminiscent of parental care. This study offers the first in-depth look at how formal and informal student care practices are intertwined in the post-Soviet educational context. The study has been published in the British Journal of Sociology of Education.